Difference between revisions of "Critical analysis: vbw-study "Folgen einer Lieferunterbrechung von russischem Gas für die deutsche Industrie" (June 2022)"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
* | * | ||
* {{Citation | title=Deutschlands Wettbewerbsstärke: Forscher warnen vor Gaskrise – Speicher jetzt zu 60 Prozent gefüllt | url=https://www.faz.net/aktuell/wirtschaft/gaslieferungen-abhaengigkeit-gefaehrdet-deutschlands-wettbewerbsfaehigkeit-18133876.html | access-date=28 June 2022}} | * {{Citation | title=Deutschlands Wettbewerbsstärke: Forscher warnen vor Gaskrise – Speicher jetzt zu 60 Prozent gefüllt | url=https://www.faz.net/aktuell/wirtschaft/gaslieferungen-abhaengigkeit-gefaehrdet-deutschlands-wettbewerbsfaehigkeit-18133876.html | access-date=28 June 2022}} | ||
| + | * https://www.spiegel.de/wirtschaft/unternehmen/russlands-gas-lieferstopp-verband-warnt-vor-wirtschaftseinbruch-um-12-7-prozent-a-cf67b579-8951-4706-9272-e60d71c03a23 | ||
| + | * https://www.manager-magazin.de/politik/deutschland/gas-stopp-russischer-gaslieferungen-koennte-deutschland-rund-13-prozent-der-wirtschaftsleistung-kosten-a-0ae39890-5c4d-425a-abca-a567f1bd936b | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 28 June 2022
Media coverage of this study:
- Deutschlands Wettbewerbsstärke: Forscher warnen vor Gaskrise – Speicher jetzt zu 60 Prozent gefüllt, retrieved 28 June 2022
- https://www.spiegel.de/wirtschaft/unternehmen/russlands-gas-lieferstopp-verband-warnt-vor-wirtschaftseinbruch-um-12-7-prozent-a-cf67b579-8951-4706-9272-e60d71c03a23
- https://www.manager-magazin.de/politik/deutschland/gas-stopp-russischer-gaslieferungen-koennte-deutschland-rund-13-prozent-der-wirtschaftsleistung-kosten-a-0ae39890-5c4d-425a-abca-a567f1bd936b
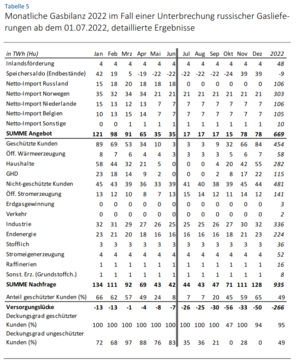
Our analysis of VBW study [1]:
- Our main critique is that the gas gap is calculated as too big, as in Table 5, depicted in the image.
- There is an underestimation of imports, which suddenly decrease in April/May
- The conversion of electricity is ignored
- No energy savings are assumed, whereas energy savings already happen
- ↑ vbw (2022), Konsequenzen eines Importstopps von russischem Erdgas, retrieved 28 June 2022