Impact/de: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) (Created page with "{{DISPLAYPAGE:Wirksamkeit}} {{:Impact}}") |
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Wirksamkeit}} |
{{:Impact}} | {{:Impact}} | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 17. Juni 2022, 06:39 Uhr
Warning: Display title "Impact on Russia" overrides earlier display title "Wirksamkeit". In short: if money from energy exports are indeed not essential to continue the war, and if embargo would really hurt Europe/the West much worse than russia, then why hasn't putin cut off the supply yet?
Impact so far[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
- In June 2022, #Russia's GDP was down 4.9% year-over-year, according to the Russian Economy Ministry. via @jakluge
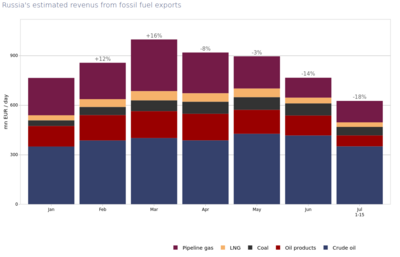
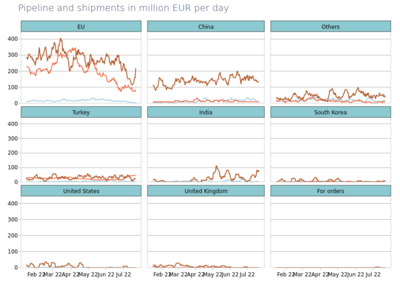
- Russian revenues from energy export decreased by ~40% in July compared to March (EU: -50%). Still, EU is paying 200 to 300 mln EUR every day! (according to CREA estimates).
- Russia gas export volumes down 3/4 compared to 2021, but profits are similar due to higher prices. OTOH profits are much lower than late 2021/early 2022, and decline sharply (via @ben_moll):
- Oil import volume has been reduced by 10 billion EUR: "Europe's Russian oil embargo: significant but not yet | Bruegel". Retrieved 2022-06-06.
- Yale School of Management: "Business Retreats and Sanctions Are Crippling the Russian Economy" (July 2022)
- Bauer, Jakob; Blickle, Paul; Ehmann, Annick; Endt, Christian; Erdmann, Elena; Grefe-Huge, Carla; Peter, Valentin; Tröger, Julius (2022-06-03). "Energiemonitor: Teuer, klimaschädlich und abhängig von Russland". Die Zeit. Hamburg. ISSN 0044-2070. Retrieved 2022-06-05.
Energy embargo[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
- "Experten: Langfristiger Gas-Lieferstopp aus Russland technisch nicht möglich". Retrieved 2022-07-19.
- Former Putin advisor Dr Illarionov said if Western countries "would try to implement a real embargo on oil and gas exports from Russia... I would bet that probably within a month or two, Russian military operations in Ukraine, probably will be ceased, will be stopped": Josephs, Jonathan (2022-04-10). "Full embargo on oil could stop war - ex-Putin aide". BBC News. Retrieved 2022-04-19.
- Schöneberg, Kai (2022-03-03). "Ökonom zu Stopp der Gaslieferungen: „Moskau droht eine akute Situation"". Die Tageszeitung: taz. ISSN 0931-9085. Retrieved 2022-03-03.
- Gurijew, Sergej; Itskhoki, Oleg (2022-03-22). "Öl und Gas aus Russland: Warum ein Embargo Wladimir Putins Krieg beenden könnte". Der Spiegel. ISSN 2195-1349. Retrieved 2022-03-22.
- Wagner, Katharina. "Ökonom Sergej Gurijew: „In so einer Lage ist Putin nie zuvor gewesen"". FAZ.NET. ISSN 0174-4909. Retrieved 2022-05-31.
- "Hohe Energiepreise: Moskau rechnet mit fast 14 Milliarden Euro Mehreinnahmen". Der Spiegel. 2022-05-28. ISSN 2195-1349. Retrieved 2022-05-29.
- Guriev; Itskhoki (2022). "The Economic Rationale for Oil and Gas Embargo on Putin's Regime" (PDF). Dropbox. Retrieved 2022-03-30.
- "Russland fördert wegen der Sanktionen des Westens immer weniger Öl". Retrieved 2022-04-29.
Embargo in general[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
- Wikipedia (2022-03-06). "2022 boycott of Russia and Belarus". Wikipedia. Retrieved 2022-03-06.
- Pennekamp, Johannes. "Ökonom Ockenfels im Interview: „Putin wird sich früher oder später über „Endgame"-Szenarien Gedanken machen"". FAZ.NET. ISSN 0174-4909. Retrieved 2022-03-16.
- Newsroom. "Kadri Simson: EU sanctions would gradually deplete Russia's oil revenues | eKathimerini.com". Retrieved 2022-03-16.
- Felbermayr, Gabriel; Mahlkow, Hendrik; Sandkamp, Alexander (2022-02). Cutting through the Value Chain: The long-run effects of decoupling the East from the West. FIW Working Paper series. FIW. Retrieved 2022-03-20.
{{cite conference}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Wirtschaftsweiser Achim Truger: "Russische Wirtschaft kann das lange aushalten"". 2022-03-30. Retrieved 2022-03-30.
- "Angriffskrieg auf die Ukraine – deutsche Wirtschaft schmiert ab". 2022-03-30. Retrieved 2022-03-30.
- "Importbeschränkungen: Zentralbankchefin: Russische Wirtschaft muss sich neu aufstellen". FAZ.NET. 2022-04-18. ISSN 0174-4909. Retrieved 2022-04-18.
- online, heise. "Halbleiter: Eine moderne russische Chipfertigung ist derzeit unrealistisch". heise online. Retrieved 2022-04-20.
- "Russland steht vor der Staatspleite: Jetzt nutzt Moskau nicht mal mehr Geld". Retrieved 2022-04-21.
- "Statistisches Bundesamt: Deutsche Exporte nach Russland sinken um mehr als die Hälfte | ZEIT ONLINE". Retrieved 2022-04-21.
- Guriev, Sergei; Itskhoki, Olivier (2022-03-24). "The economic rationale for an oil and gas embargo on Putin's regime". bne IntelliNews. Retrieved 2022-04-22.
- "SanctionsWorkingGroup-ActionPlan.pdf". Google Docs. Retrieved 2022-04-24.
- "High-level Impact of Sanctions on Russian Economy - April 2022.pdf". Google Docs. Retrieved 2022-04-24.
- Wagner, Katharina. "Sanktionen gegen Russland: Langer Atem gegen Putin". FAZ.NET. ISSN 0174-4909. Retrieved 2022-05-25.
- Bathon, Roland (2022-05-28). "Sanktionen gegen Russland: China baut Moskwitsch 2.0 in ehemaligem Renault-Werk". Der Freitag. ISSN 0945-2095. Retrieved 2022-05-28.
- Russian airlines strip jets for spare parts as Ukraine war sanctions hit industry, 2022, retrieved 9 August 2022