Difference between revisions of "Critical analysis: vbw-study "Folgen einer Lieferunterbrechung von russischem Gas für die deutsche Industrie" (June 2022)"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| − | + | Our analysis of VBW study <ref> {{Citation | vauthors=vbw | year=2022 | title=Konsequenzen eines Importstopps von russischem Erdgas | url=https://www.vbw-bayern.de/vbw/Themen-und-Services/Energie-Klima/Energie/Folgen-einer-Lieferunterbrechung-von-russischem-Gas-f%C3%BCr-die-deutsche-Industrie.jsp | access-date=28 June 2022}}</ref>: | |
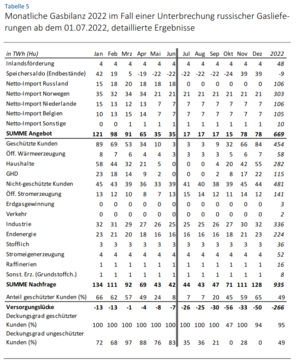
| − | * Our main critique is that the gas gap is calculated as too big | + | * Our main critique is that the gas gap is calculated as too big, as in Table 5, depicted in the image. |
| − | ** There is an underestimation of imports, which suddenly | + | ** There is an underestimation of imports, which suddenly decrease in April/May |
** The conversion of electricity is ignored | ** The conversion of electricity is ignored | ||
** No energy savings are assumed, whereas energy savings already happen | ** No energy savings are assumed, whereas energy savings already happen | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 21:53, 28 June 2022
This study has been cited by:
- Deutschlands Wettbewerbsstärke: Forscher warnen vor Gaskrise – Speicher jetzt zu 60 Prozent gefüllt, retrieved 28 June 2022
Our analysis of VBW study [1]:
- Our main critique is that the gas gap is calculated as too big, as in Table 5, depicted in the image.
- There is an underestimation of imports, which suddenly decrease in April/May
- The conversion of electricity is ignored
- No energy savings are assumed, whereas energy savings already happen
- ↑ vbw (2022), Konsequenzen eines Importstopps von russischem Erdgas, retrieved 28 June 2022